Introduction
The modern trade finance environment is changing faster than ever before, driven by the need for efficiency, accuracy, and transparency. Manual and disjointed traditional processes struggle to keep pace with the increasing transaction volumes and intricate regulatory requirements. Organizations can use trade finance process automation to automate operations throughout the full trade lifecycle, including the issuance and settlement of a trade. AI-based solutions reduce risks, improve workflows, and offer real-time visibility in addition to accelerating them, which is why the future of trade finance looks entirely different.
Persistent Challenges in Traditional Trade Finance
Traditional trade finance continues to grapple with structural inefficiencies that hinder the automation of the trade finance process and visibility across the trade lifecycle.
A massive shortage of available trade finance is one of the urgent problems. The 2023 "Trade Finance Gaps, Growth, and Jobs Survey" released by the Asian Development Bank showed that in 2022, the global trade finance gap was USD 2.5 trillion. In the case of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), rejection rates are very high; about 45% of SME trade finance applications were rejected by banks.
-
Heavy reliance on manual, paper-based processes
A trade finance operation can attract over one hundred pages of documentation. The volume of physical documents alone decreases the speed of validation, the possibility of errors, and tracking.
-
Regulatory and compliance hurdles
Compliance and sanctions screening, as well as AML (Anti-Money Laundering) costs, are increasing. Lots of banks complain of difficulty in steadfast regulatory compliance in diverse jurisdictions, making the checks more difficult to streamline or mechanize.
-
Disparity between SMEs and larger firms
SMEs not only suffer disproportionately in terms of rejection rates but also in terms of failing to provide collateral, information, or established banking relationships to meet demands. They usually lose not due to a weak deal in terms of trade, but due to the fact that the current models of credit and risk assessment are not suitable for them.
AI-Powered Automation & Streamlining the Trade Lifecycle
Automated trade finance processes based on AI are no longer a thing of experimentation in the field of trade finance. It is being integrated into the core processes of document verification to payment execution, which are changing the trade lifecycle into a more transparent, quicker, and reliable process.
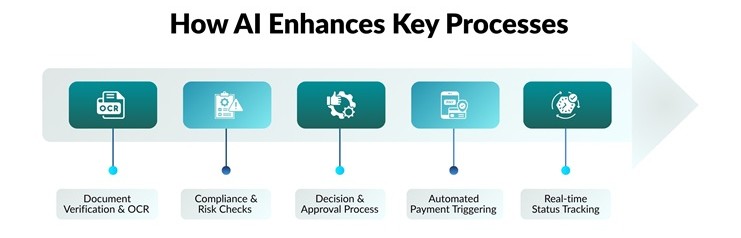
How AI Enhances Key Processes
-
Document verification & OCR: AI reads, categorizes, and authenticates trade documents (e.g., letters of credit, bills of lading) to find discrepancies or fields that are absent. This will minimize human error and hasten preliminary checks.
-
Compliance & risk checks: Rule-based logic and machine learning flag fraud, AML concerns, or regulatory non-compliance before they halt transactions.
-
Decision & approval process: AI automatically uses predefined criteria and only escalates human intervention where necessary, reducing the delay time by a factor.
-
Automated payment triggering: Payments are automatically released without manual release once given conditions (such as shipping documents received) are met.
-
Real-time status tracking: Seller, buyer, carrier, and bank coordination is enhanced by participants in the lifecycle by seeing the latest status in real time.
AI in the Trade Lifecycle
| Lifecycle Stage |
AI / Automation Role |
Benefit |
| Issuance & Approval |
Automatic checks on trade partners, credit, and texts |
Faster approvals, fewer term mismatches |
| Shipping & Logistics |
Auto-triggered document flow, shipment status tracking |
Reduced follow-ups, timely alerts |
| Payment & Settlement |
Payment is released when contractual conditions are met |
Fewer delays, less manual reconciliation needed |
Measurable Gains
-
AI-driven automated document processing saves close to 60 percent of the time spent on manual processing.
-
About one-third of banks are currently deploying AI or machine learning in live client trade finance transactions, which is an increase to 45 percent as of 2025, compared to one-third last year.
-
In February 2024, Lloyds Bank finalized an entirely digital documentary collection using both electronic Bills of Lading (eBLs) and digital Promissory Notes (dPNs), saving time taken to complete the transaction by 15 days to 24 hours.
Risk Management and Compliance Through AI
AI enhances control by incorporating intelligent control throughout the trade lifecycle. AI is a major pillar of risk resiliency in the trade finance field, where a single compliance slip could result in significant fines or a damaged reputation.
Smarter Risk Detection, Real Time
-
AI systems can track transaction patterns, flows, and document streams in real time to identify anomalies or fraud or suspicious behavior faster than humans.
-
These systems are adaptive and will flag counterparty risks according to changing data, as opposed to risk scores that are fixed.
-
In trade activities, this implies automated investigations of credit exposures, payment abnormalities, or anomalous shipping documents.
Enforcing Compliance without Latency
-
AI imposes limitations dynamically, like regulatory constraints, lists of sanctions, and limits of jurisdiction that can be coded and checked at all times.
-
It will automate document validation (e.g., invoices, letters of credit) and make every step of a workflow comply with internal and external policies.
-
Rules or regulatory amendments are easy to implement and reduce the time lag between enacting rules and their implementation.
Governance, Oversight, and Model Integrity
-
A governance system is necessary to have effective AI-based compliance, like model testing controls, model validation controls, audit trail controls, and human control.
-
The absence of such mechanisms can result in AI systems' bias, a lack of reasoning behind decisions, or increased areas of non-compliance.
Cost and Time Efficiency Gains
The trade lifecycle process automation provides quantifiable time and cost savings. Automated systems can also save firms money by a huge margin on manual labor, and they are also able to improve throughput when automated systems are applied in carrying out routine tasks like document verification, approvals, and compliance checks.
Key gains include:
-
A case study of automating trade finance processes at DBS Bank revealed an 85 percent decrease in processing time (reducing turnaround time of 2-3 days to only a matter of hours) and a 40 percent decrease in operating costs; the error rate dropped to approximately 0.8 percent in document processing.
-
In Bruckner Group, the L/C price confirmation workflow was automated and allowed cost savings of 30-40 percent and transformed a 5-day process into a substantially shorter digital cycle.
-
Other banking industry data indicate that smart automation can cut average handling time by 60 percent, release 50 percent of full-time equivalents (FTEs) of employees to do higher-order work and provide full operational visibility.
Emerging Trends and the Future of AI in Trade Finance
The integration of AI and automation into the trade lifecycle is accelerating, with the World Trade Organization (WTO) projecting that global trade could increase by 34-37 percent by 2040, driven by advancements in logistics, compliance, and communication.
The Future of AI-Based Trade Finance
-
Predictive analytics becomes prescriptive: Models will not only predict risk, they will also prescribe the best way to structure or dynamically cap credit limits or prioritize a workflow throughout the lifecycle of trade.
-
Large language models (LLMs) in trade logic: Recent progress in financial LLMs is contributing to the parsing of the terms of complex contracts, interpreting regulatory documents, and machine translation reporting stories.
-
Inclusive access and regulation: Trade finance process automation benefits will be skewed to more developed markets unless policy and infrastructure efforts are made to advance the idea. The World Trade Organization (WTO) cautions against expanding the disparities across the globe without the use of AI in a non-inclusive manner.
Conclusion
The trade lifecycle is increasingly being redefined by AI and automation to form new, faster, more reliable, and transparent systems. The automation of trade finance processes through the integration of intelligence will improve compliance, minimize errors, and liberate resources to be used in strategic priorities. With a faster pace of adoption, early adopters will gain a competitive advantage, as they will be in a higher position to achieve efficiency and resilience in a digitally dynamic trade environment. The future is facing a smarter trade finance that is seamlessly connected.

