Introduction
Investment banking requires an accurate valuation of a company so that the right decisions can be made. The EV/EBITDA ratio plays an essential role in this process, as it presents a more comprehensive and easily comparable indicator of a company's financial condition and performance. This ratio compares Enterprise Value (EV) with Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA) to analyze the company's operational efficiency. It is helpful in many valuation models.
EV/EBITDA Ratio: A Critical Valuation Tool
The EV/EBITDA ratio can be used as one of the most significant indicators of investment banking to compare a company's value with the market and estimate its potential for future growth. This ratio gives a good insight into the company's financial standing and worth. It is beneficial when comparing different companies across industries as it is expressed in a uniform manner.
-
Enterprise Value (EV) refers to the total worth of a company, which can be arrived at through market capitalization, debt, and cash. EV is a more holistic approach to valuation than market capitalization because it includes the company's obligation in terms of debt.
-
EBITDA is a financial ratio that shows a company's operational profitability before taking into account its financial management, taxes, and depreciation or amortization. It is the most fundamental measure of the company's ability to generate profit.
As an investment banker, the EV/EBITDA ratio proves useful because it is calculated by dividing EV by EBITDA. This ratio reveals a company's value based on its capability to generate earnings.
Why the EV/EBITDA Ratio Matters in Valuation?
As an instrument in company valuation, the EV/EBITDA has a clear and standardized method of determining a company's worth and potential for future development and growth. It is particularly useful because it offers insight that is not available with other ratios and reveals a business's capital structure and operating profitability.
-
Holistic Financial Snapshot: Unlike the P/E ratio, which factors in net earnings only, the EV/EBITDA ratio takes into account the broader definition of a company's value by adding net debt and cash to the balance sheet.
-
Cross-Industry Comparisons: This ratio is quite recommendable when comparing firms in different industries where the effect of capital structure and taxation has been eradicated; hence, it will be easier to establish industries with different debts or taxes.
-
Indicator of Market Expectations: A high EV/EBITDA reflects the fact that the market anticipates future growth, while a low one may suggest undervaluation or possible hazards. Thus, it is an essential factor in the selection of investment opportunities.
What Does EV/EBITDA Tell You?
The EV/EBITDA ratio is one of the most widely used ratios in assessing a company's financial performance and market capitalization. It helps to understand the performance of a particular company concerning its profitability and the price that is given to it in the market. Here's what this ratio reveals:
-
High EV/EBITDA Ratio: A higher ratio usually implies that a company is costly in terms of earnings per share, which may indicate high market expectations for future growth. This can also mean investors are willing to fork out extra cash for the company's earnings prospects.
-
Low EV/EBITDA Ratio: On the other hand, a lower ratio may suggest that a firm is currently undervalued or that the market has lower expectations for the firm's growth. It could indicate market cynicism or possible underpricing, which may be a good chance for investors to buy assets at a low price.
The EV/EBITDA ratio is also helpful when comparing companies in different industries. By normalizing the valuation metrics, it is easier to conduct a cross-industry comparison. However, it is crucial to understand that the ratio should be viewed in the context of specific parameters, including the condition of the market and the state of the particular company. Thus, T this approach makes the ratio's findings an integral part of the overall valuation process and improves investment decisions.
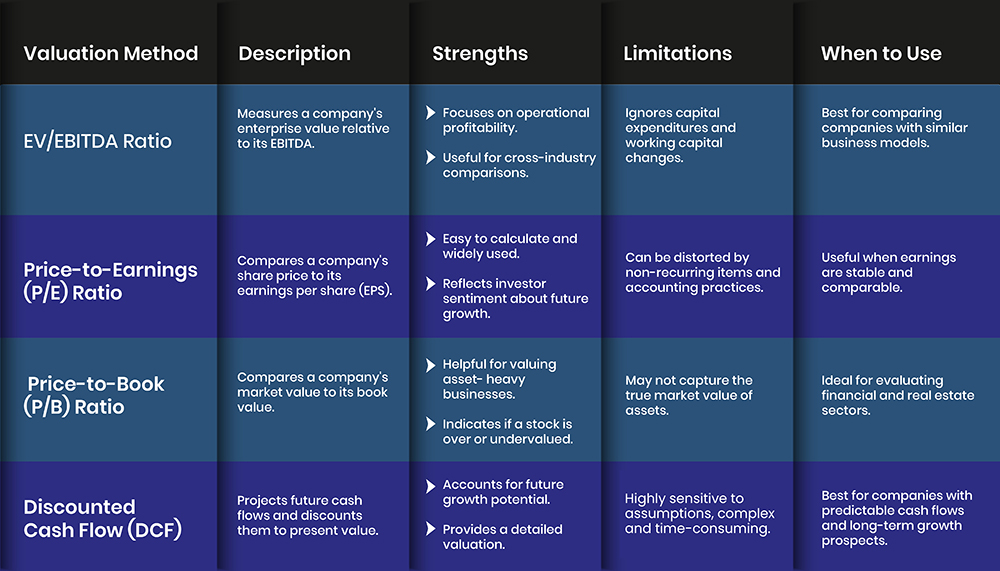
Comparing the EV/EBITDA Ratio with Other Valuation Methods
The EV/EBITDA ratio is a popular valuation metric, but it is essential to understand its advantages and disadvantages by comparing it with similar methods. Here's a detailed comparison:
-
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio:
The P/E Ratio is calculated by dividing the price of a share by its earnings per share (EPS). While the EV/EBITDA ratio considers the capital structure and debt, the P/E Ratio only considers equity value. This makes the P/E Ratio less complete when a company has a lot of debt or depreciation, and amortization are not on the same scale.
-
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio:
The P/B Ratio is the ratio of the market price of a company's stock to its book value per share. It is especially important for companies with many fixed assets, but it does not take into account earnings performance or the effect of capital structure. The EV/EBITDA ratio gives a better picture of the company's efficiency and returns from operations.
-
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis:
The DCF analysis entails predicting a firm's future cash flows and then using these to determine their present value. Despite DCF providing a detailed intrinsic value estimation, this is a compassionate model for assumptions and inputs. On the other hand, the EV/EBITDA ratio offers an easier and quicker way of generating a comparative figure without making many forecasts.
Collectively, the EV/EBITDA ratio is preferred due to its ease of use in comparing the performance of firms with different capital structures. However, it is more useful when combined with other models to produce an overall picture of a company's worth.
Practical Application: Using the EV/EBITDA Ratio in Real-World Valuation
The EV/EBITDA ratio is a practical valuation metric in the real world and offers a straightforward way of assessing and comparing the financial position of firms. To effectively utilize this ratio, start with the following steps:
-
Data Collection: Collect the company's financial information under consideration for the evaluation. The enterprise value (EV) calculates the value of a company's equity and its debt minus the cash and earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA).
-
Calculation: Compute the EV/EBITDA ratio using the formula:
EV / EBITDA = Enterprise Value (EV) / EBITDA
For example, if a company has an EV of USD 500 million and its EBITDA is USD 50 million, the ratio will be 10. This shows that investors are willing to pay for the company's total enterprise value at ten times its EBITDA.
-
Benchmarking: Compare the calculated ratio to its industry peers or past years' data. This allows for determining whether the company is over- or undervalued in comparison with the other members of the industry. Sometimes, a higher EV/EBITDA ratio means that the stock is overpriced due to increased growth prospects or better positioning in the market.
-
Contextual Analysis: It is also essential to examine the company's growth potential, the market environment, and industry factors. For instance, a high ratio in a high-growth industry may be reasonable, while the same may be a cause of concern in a slow-growing industry.
The integration of the EV/EBITDA ratio into other valuation models enriches the analysis and improves the decision-making of investment bankers and analysts. Knowing the ratio's meaning in different activities can help assess a company's financial position and market worth.
Conclusion
The EV/EBITDA ratio continues to be one of the most fundamental valuation methods in investment banking. Therefore, its effectiveness as an informative tool that highlights the structure of financial statements and market expectations is unparalleled. However, it remains a rough measure. The EV/EBITDA ratio provides a measure of comparability in a way that is not necessarily available from other metrics. Changing investment environments make it imperative that this ratio is well understood and managed for successful investments to be conducted in the future.

