Introduction
Investment banking has a significant impact on the international financial sector, as firms are typically categorized as either bulge bracket or boutique banks. Their functions are essential, but their operations, audience focus, and strategies differ significantly. Professionals, investors, and clients must know the differences between boutique and bulge-bracket institutions. This article examines the key aspects of these two organizations, their operational models, and their evolving roles in today’s economic climate, providing a clear and concise explanation.
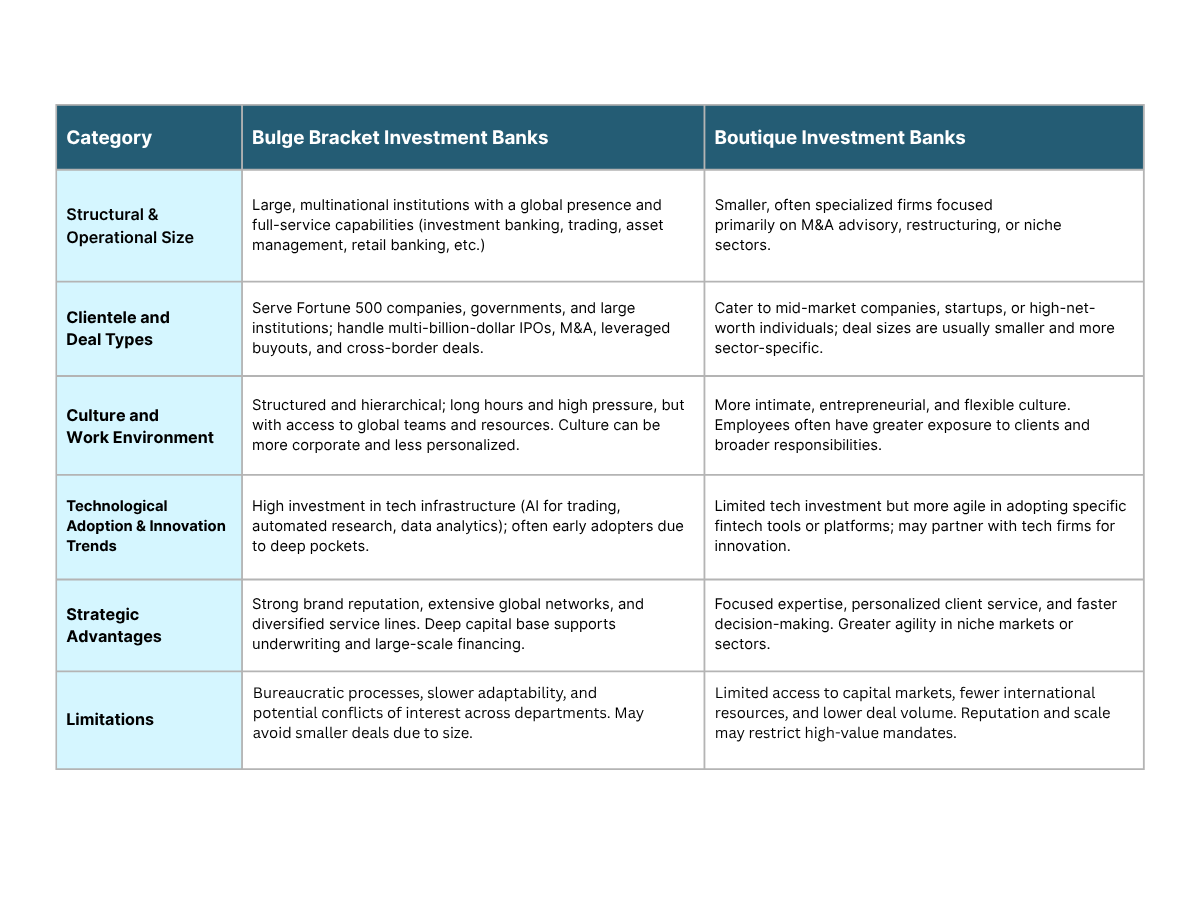
Structural and Operational Differences Between Bulge Bracket and Boutique Banks
Professionals, clients, and investors involved in investment banking need to understand the structural and operational differences between bulge-bracket and boutique banks. Although both financial advisors and capital markets serve essential functions in these sectors, their working methods differ significantly in terms of size, structure, and the manner in which they assist clients.
-
Scale and Global Reach :
Bulge bracket banks are massive multinational organizations that operate globally, employ thousands of staff, and offer a wide range of services. They have a cross-continental reach, backing transactions in basically all of the major markets. Boutique banks, on the other hand, are smaller and more regionally focused. They tend to cater to specialized markets or serve specific industries with specialized knowledge.
-
Service Offerings:
Bulge bracket firms offer a comprehensive range of financial services, including investment banking, trading, research, underwriting, lending, and asset management. Conversely, boutique firms often focus on a more limited set of services, most commonly M&A advisory or restructuring, to clients who prefer customized advice over the diversification offered by bulge bracket firms.
-
Organizational Structure:
A hierarchical, layered structure, well-defined roles, compliance systems, and slow decision-making chains characterize bulge brackets. Boutiques also have flatter hierarchies, which allow them to communicate quickly and engage directly with seniors as well as be more flexible when executing deals.
-
Resource Allocation :
Major institutions allocate a substantial amount to internal infrastructure, encompassing risk management, technology systems, and regulatory compliance. Boutique banks direct resources to customized client service, industry-oriented research, and tailored solutions as opposed to commoditized operational systems.
Clientele and Deal Types: Contrasting Market Focus
The unique differences in clientele and types of deals between the two types of banks stem from their sizes and positions in the industry. Most of the time, bulge bracket banks handle financial transactions for large corporations, countries, and institutions. On the other hand, boutique banks primarily work with mid-market firms, businesses, and individuals who have substantial financial resources and require specialized financial guidance.
-
Client Base:
Bulge-bracket banks generally work with Fortune 500 corporations, multinationals, and large institutional investors. Boutique banks, on the other hand, may specialize in mid-market companies, family-owned businesses, and emerging growth companies, which require niche services.
-
Deal Size and Structure:
Bulge brackets specialize in high-value transactions that involve multiple nations, such as multi-billion-dollar mergers, IPOs, and complex debt offerings. Boutique firms primarily focus on smaller, strategic transactions, including private placements, targeted acquisitions, and the exit of founders.
-
Market and Industry Focus:
Boutique banks tend to develop profound sector specialization, typically in healthcare, technology, or consumer sectors, whereas bulge brackets offer diversified coverage across all global markets and industries.
Culture and Work Environment: How Boutique vs Bulge Bracket Banks Differ
The environment inside a company is much different in the boutique vs bulge bracket competition. They play a role in both employee morale and customer interactions, as well as team building and future career advancement. Although they both strive for results, the way they handle teamwork, structure, and their personal lives is quite different.
-
Team Structure and Collaboration:
The small and flat organizational structure of boutique banks allows analysts and associates to communicate easily with senior staff members and customers. This approach enables employees to learn more, act more quickly, and assume greater responsibility from the outset of their careers. In contrast, junior workers in bulge bracket banks often have less exposure to top-level talks due to the bank’s structured hierarchy.
-
Client Engagement and Ownership:
Since boutique firms typically have a small number of employees, those at these firms often handle their client relationships. As a result, employees begin to feel more responsible for their actions. At bulge bracket institutions, it is typical for client access to be reserved for senior staff, while junior staff manage research and assist in executing deals.
-
Work Intensity and Hours:
High demands for time can be found in both places, but being part of a boutique can give more freedom due to fewer administrative hurdles. Unlike weighty brackets, bulge brackets focus on robust structures and addressing transactions that require attention at any time of day.
-
Learning and Mentorship:
Learning in a boutique involves getting direct help and feedback from partners. At the same time, bulge brackets have planned training and allow staff to train in different countries, even if mentorship is usually less unique.
Technological Adoption and Innovation Trends in Bulge Bracket vs Boutique Banks
The investment banking scene is rapidly evolving due to technological advancements, and both bulge-bracket and boutique banks are implementing new technologies to enhance efficiency and service to clients. Whereas bulge bracket banks can utilize their enormous resources to incorporate the latest technologies at scale, boutique banks may be more concerned with small, agile technology applications that can be tailored to their specific advisory practices.
-
Investment Scale and Infrastructure:
Bulge-bracket banks typically have substantial budgets to develop sophisticated analytics, AI-based risk management, and automated trading systems. Their wide-scale infrastructures facilitate worldwide operations and the processing of complex transactions, enabling quicker decisions and enhanced precision in various markets.
-
Customization and Agility:
Boutique banks focus on flexible technology to improve customized client relationships and specialist market analysis. They are also smaller and can thus adapt more quickly, utilizing innovative fintech tools that enhance deal sourcing, valuation modeling, and communication, without the need for extensive bureaucracy.
-
Competitive Edge Through Digital Transformation:
Both types of banks utilize technology to enhance compliance, cybersecurity, and data management. Bulge bracket banks, however, prioritize an entire regulatory reporting system, whereas boutiques concentrate on solutions that simplify deal execution and client cooperation.
Strategic Advantages and Limitations in Boutique vs Bulge Bracket Banks
The strategies employed by boutique and bulge-bracket investment banks have a significant impact on their success in the financial environment. Compared to others, bulge bracket banks have additional privileges, tools, and expertise for handling large transactions globally. Alternatively, being agile and focused, boutique banks give their clients highly individualized financial guidance.
-
Boutique banks focus on specific sectors, offering personalized services through senior-level involvement and deep industry expertise. Bulge bracket banks provide broader coverage across industries, but their scale often results in standardized solutions and less individualized attention.
-
While boutique firms are agile and highly customized, they often lack the capital, infrastructure, and global presence to handle large or complex transactions, and face heavier strain from regulatory compliance. Bulge brackets, with larger resources and dedicated compliance teams, manage these challenges more efficiently but may suffer from internal bureaucracy.
-
Boutiques compete through agility, niche focus, and high-touch client engagement. Bulge bracket banks differentiate by offering full-service capabilities, global execution strength, and the ability to handle high-value, multi-layered deals.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between the bulge bracket and boutique investment banks is crucial for anyone involved in financial matters. They differ mainly in their operating area, the clients they serve, corporate culture, employee compensation structure, growth strategies, and their use of technology. Although bulge brackets have a global range and many resources, boutiques focus on specific matters and move quickly. As digital advancements and the market continue to progress, a firm must choose between boutique and bulge-bracket banks based on its exact goals, requirements, and aspirations.

